<?xml encoding=”UTF-8″>
Men’s Health: Prostate Cancer Side Effects, Prevention and Cure
It’s very important to note that Prostate Cancer is a very very large topic we makes it impossible to discuss all of it there are also a lot of controversial aspects of Prostate Cancer so even what I will talk about may seem confusing at times but I will try to make things as clear as possible.
In this article, we attempt to give you a basic understanding of what Prostate Cancer is how we can diagnose it or take steps to prevent it.
We also present our different options to treat Prostate Cancer naturally through diet or medically with some of the well-known side effects.
Finally we discuss the options for treating advanced Prostate Cancer.
What is Prostate Cancer?
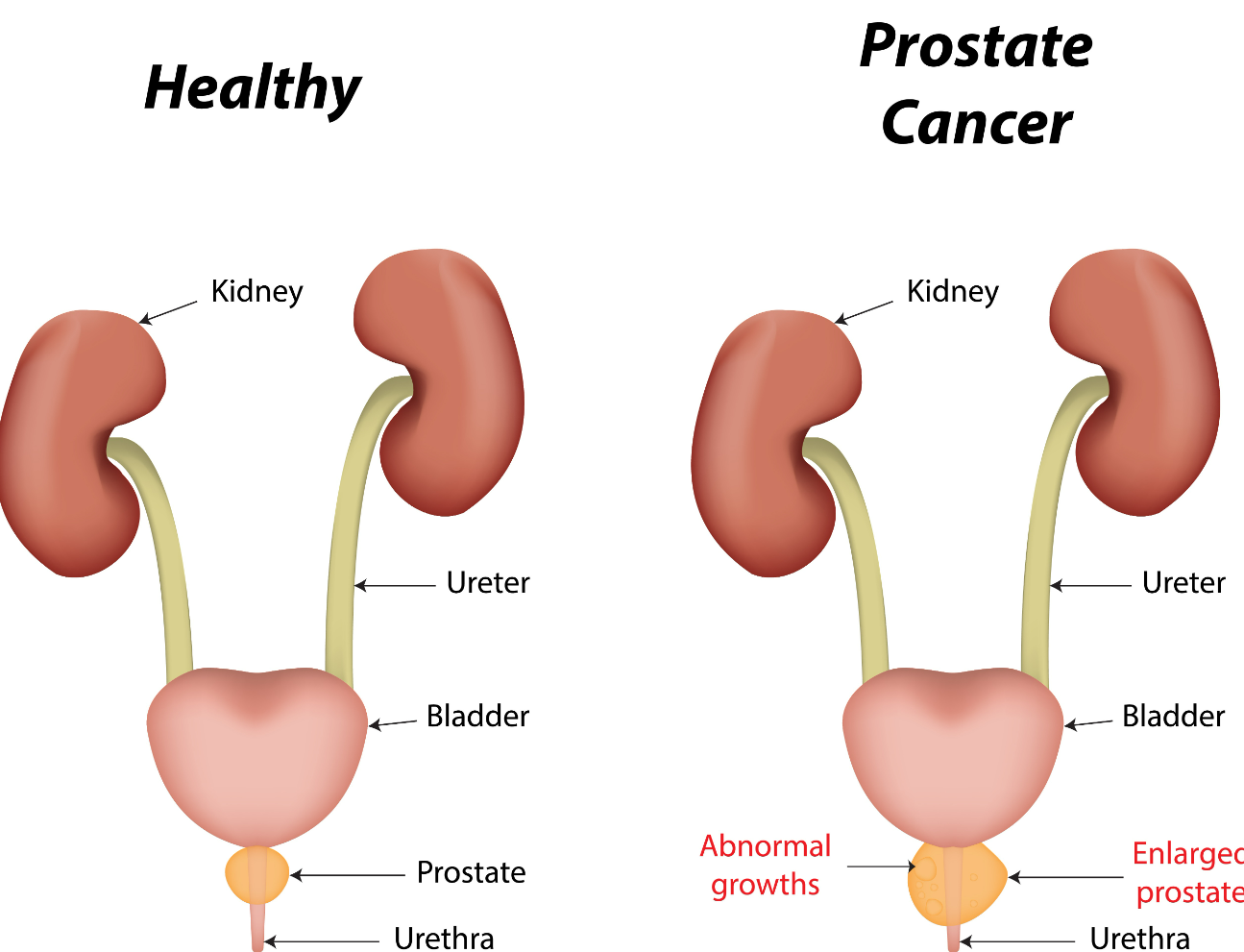
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate gland of men. Prostate Gland is a small gland in the male reproductive system located below the bladder and in front of the rectum, and its main function is to produce and store seminal fluid. This fluid is part of semen and helps to nourish and transport sperm.
Prostate cancer can vary in severity, and some cases may grow very slowly and not require treatment, while others may grow quickly and spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms of prostate cancer can include difficulty urinating, weak or interrupted urine flow, blood in the urine or semen, and pain or discomfort in the pelvic area.
What Causes Prostate Cancer in Men?
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland begin to grow uncontrollably and form a tumor. This cancer can spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones, lymph nodes, and organs, if left untreated.
There are different types of prostate cancer, which are classified based on how the cancer cells look under a microscope. The most common type of prostate cancer is adenocarcinoma, which develops in the cells that produce the prostate fluid.
Other types of prostate cancer include small cell carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma, and sarcoma.
What are the Types of Prostate Cancer?
There are different types of prostate cancer, which are classified based on how the cancer cells look under a microscope. The most common type of prostate cancer is adenocarcinoma, which develops in the cells that produce the prostate fluid. Other types of prostate cancer include small cell carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma, and sarcoma.
Prostate cancer may not cause any symptoms in its early stages, but as the cancer grows, it can cause symptoms such as difficulty urinating, a weak urine flow, blood in the urine or semen, pain in the back, hips, or pelvis, and erectile dysfunction.
Risk factors for prostate cancer include age (most cases occur in men over 65), family history, race (African American men are at higher risk), and certain genetic mutations.
Treatment for prostate cancer depends on the stage of the cancer and may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or a combination of these approaches. In some cases, active surveillance (also called watchful waiting) may be recommended, in which the cancer is monitored but not immediately treated.
What are the Types of Prostate Cancer?
There are several types of prostate cancer, which are classified based on the appearance of the cancer cells under a microscope. The most common type of prostate cancer is adenocarcinoma, which accounts for over 90% of all cases. Other less common types of prostate cancer include:
- Small cell carcinoma: This is a rare and aggressive type of prostate cancer that is similar to small cell lung cancer. It tends to grow and spread quickly, and is typically more difficult to treat than adenocarcinoma.
- Transitional cell carcinoma: This is a type of cancer that usually begins in the cells lining the bladder and can spread to the prostate gland.
- It is relatively rare and accounts for less than 1% of prostate cancers.
- Sarcoma: This is a rare type of cancer that can develop in the connective tissue of the prostate gland. It is typically more aggressive than adenocarcinoma.
- Neuroendocrine tumors: These are rare tumors that can develop in the prostate gland and can produce hormones. They are typically more aggressive than adenocarcinoma.
It’s important to note that most prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas, and the treatment options for the other types of prostate cancer may differ from those for adenocarcinoma. It’s also possible for more than one type of cancer to be present in the prostate gland. Your doctor will be able to determine the type of prostate cancer you have through a biopsy and pathology analysis of the cancer cells.
Should You Be Worried About Prostate Cancer?
The real question here is do you have prostate glands?
O yes! Then you should equally be worried about suffering from Prostate Cancer.
If you have a prostrate gland, which is a gland which is part of the male genital urinary system that produces prostatic fluid. This fluid is alkaline in nature and makes up about a quarter of semen and helps sperm survive in the acidic vagina of female.
Prostate Cancers are the most common cancer in Men aside from skin cancer and among the different types of Prostate Cancers, 95% of Prostate Cancers are Adenocarcinoma.
However Prostate Cancer is still the second most common cause of cancer death in Men after lung cancer. Until Recently, It was generally understood to be regularly screened for Prostate Cancer.
The main point of screening was to catch the cancer it is early development stage since it’s very rare to have symptoms of Prostate Cancer unless the disease is already in the very advanced stage.
The healthy recommendation is that men over 50 years of age should screen annually for Prostate Cancer. And if you are African American of have a history of Prostate Cancer, then you should screen for Prostate Cancer at a much earlier age of 40 years old.
What are the different ways to treat Prostate Cancer?
Examples of treatments for prostate cancer include:
- Radical prostatectomy: Surgery to remove the entire prostate gland.
- External beam radiation therapy: High-energy radiation is directed at the prostate gland from outside the body.
- Brachytherapy: Radioactive seeds or pellets are implanted directly into the prostate gland to kill cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy: Medications are used to block the production or action of male hormones that can stimulate the growth of prostate cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Drugs are used to kill cancer cells or slow their growth.
- Immunotherapy: A type of treatment that stimulates the immune system to attack cancer cells.
- Cryotherapy: The prostate gland is frozen with a probe to kill cancer cells.
- Naturally through diet and lifestyle changes.
- Health Supplement for Prostate Cancer.
It’s important for men to discuss prostate cancer screening with their healthcare provider, particularly if they have risk factors for the disease. Screening tests may include a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test or a digital rectal exam.
With the anvancement in Health and Supplement, we now have some Men’s health supplement for Prostate Glad issues. This Men’s health Supplement called Uricot is one of the most popular supplement that is commonly available. Click the link to learn more about this Prostate Gland Supplement.
What are some of the preventative measures of Prostate Cancer?
While there is no surefire way to prevent prostate cancer, there are several steps men can take to reduce their risk of developing the disease. One of the most important things men can do is to maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking. Men should also be aware of their family history of prostate cancer and discuss their risk with their healthcare provider. Regular screening for prostate cancer, such as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test or a digital rectal exam, may also help detect the disease early when it is more treatable. However, the benefits and risks of screening should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for each individual.
Additionally, some studies have suggested that certain dietary supplements, such as vitamin E and selenium, may help reduce the risk of prostate cancer, but more research is needed to confirm these findings.
In the next articles, we will discuss more about some recent and natural ways to treat Prostate Cancer and the Lifestyle changes you could make to prevent or ultimately delay you have Prostate Cancer.
Right here is the right blog for anyone who would like to understand this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually will need toÖHaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin on a subject thats been discussed for years. Wonderful stuff, just great!